What is logistics software development?


Transportation software development is the convergence of technology and logistics, dedicated to resolving the multifaceted challenges faced by transportation and logistics companies as they manage extensive data and navigate the complexities of supply chain logistics. Incorporating advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, IoT, and robust data analytics, this field empowers organizations to streamline, automate, and optimize processes within transportation and supply chain domains. Its core objective lies in crafting tailored digital solutions to enhance decision-making, improve resource utilization, minimize operational costs, and ultimately deliver superior services to customers.
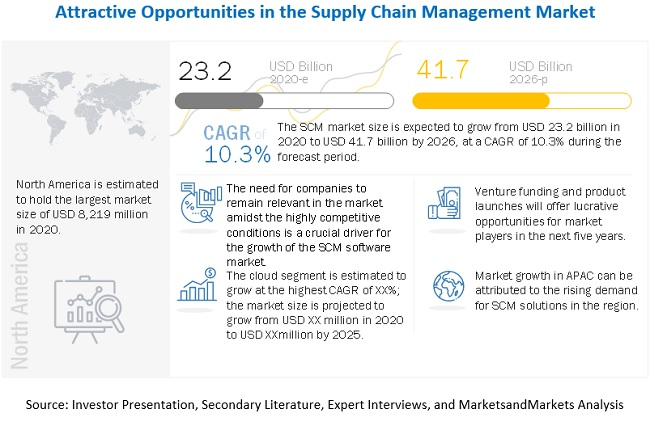
Efficiency within the entire supply chain is fundamental for a company’s profitability, customer satisfaction, and competitive edge. An efficient logistics system minimizes costs, waste, and boosts productivity, enabling prompt and precise product delivery, thereby transforming overall customer experience. Achieving this involves intricate logistics integration, precise data analysis, and the adoption of cutting-edge technologies. With sophisticated solutions like Transportation Management Systems (TMS), Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), logistics industry players can implement best industry practices, automate tasks, and gain real-time insights, ensuring agility in adapting to market shifts. Emerging technologies such as IoT, blockchain, AI, and predictive analytics are shaping a future of adaptive and resilient supply chains. According to MarketsandMarkets™, the anticipated surge in the Supply Chain Management Market from USD 23.2 billion in 2020 to USD 41.7 billion by 2026 is driven by a growing need for amplified operational visibility, cloud-based SCM adoption among SMEs, eCommerce expansion, and AI integration, promising an innovative ecosystem tailored for dynamic growth.
In the present market, a wide range of software solutions addresses business challenges across various industries, emphasizing niche industry expertise. In the logistics sector, notable software types include:
TMS solutions specialize in managing multiple logistical tasks. These systems excel in optimizing routes, selecting carriers, and providing real-time tracking capabilities. Their primary objective is to facilitate efficient, cost-effective, and transparent transportation of goods.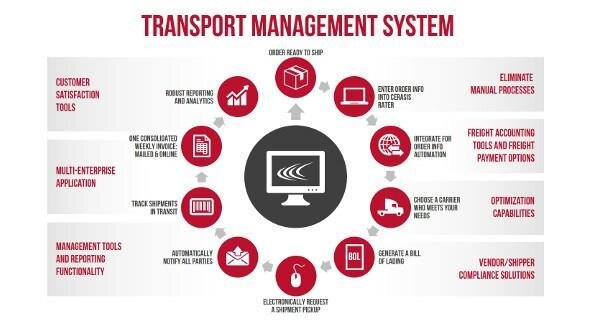
WMS software focuses on overseeing and controlling warehouse operations. It handles tasks such as inventory tracking, order processing, picking, packing, and shipping within warehouse facilities.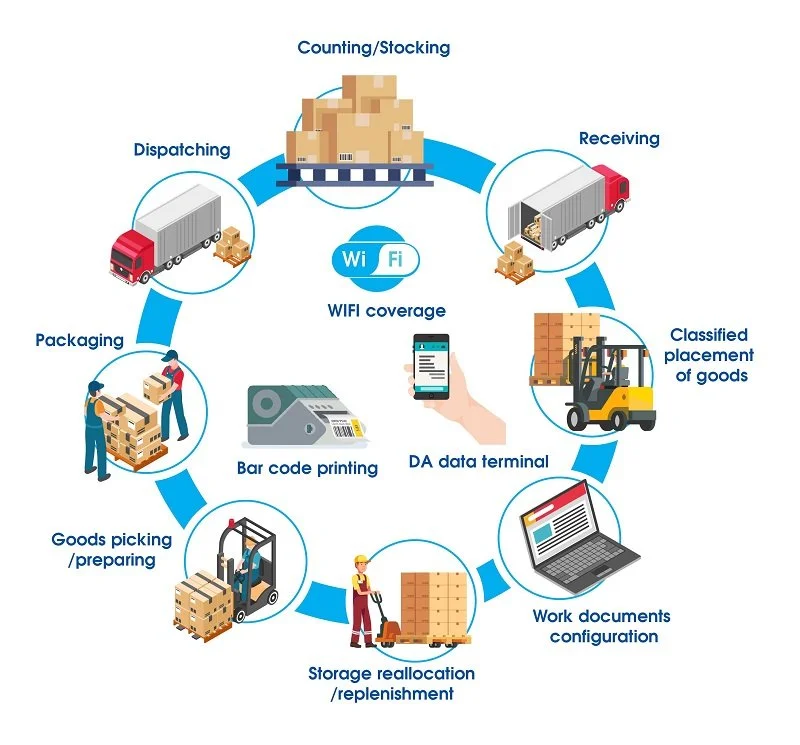
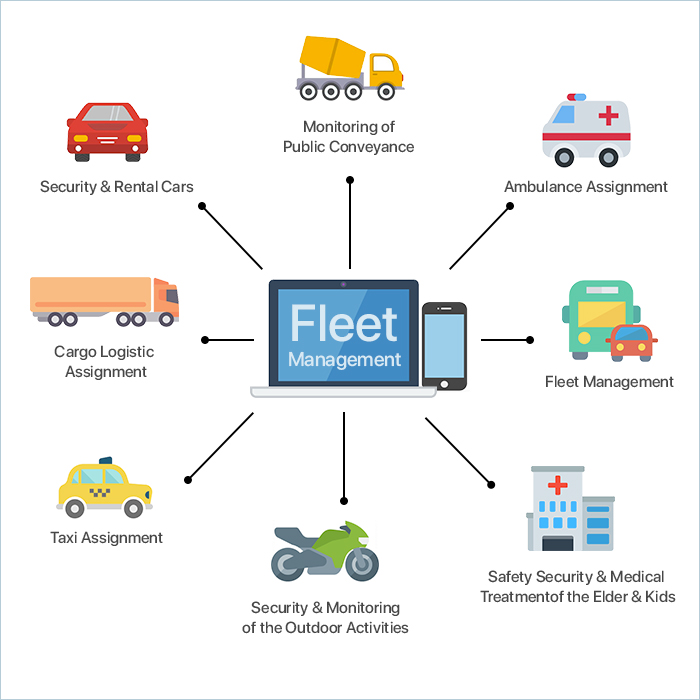
Fleet management software development solutions are crafted to assist in overseeing and monitoring inventory levels while managing the movement and maintenance of a fleet of vehicles, aiding project managers in optimizing operations. These solutions streamline inventory control, monitor stock levels, and ensure the efficient operations of fleets.
Route optimization software, powered by location data analysis, meticulously examines diverse factors including traffic patterns, delivery destinations, and vehicle capacities. Leveraging this information, it calculates the most efficient routes, minimizing fuel costs and time spent while guaranteeing punctual deliveries, thereby enhancing logistics efficiency.
In the realm of logistics, innovation thrives on the back of advancing technologies that redefine industry standards and operational methodologies. Recent research highlights the pivotal role played by several technological marvels, propelling the logistics sector forward.
IoT’s transformative impact on supply chain visibility extends beyond real-time updates on shipments and deliveries. It significantly enhances location and route management, improving inventory oversight, storage conditions, and predictive maintenance. The integration of 5G technology further amplifies IoT’s potential in logistics, fostering more sophisticated operations and enabling enhanced business intelligence.
Embracing cloud based software solutions enables scalability based on market demands, offering flexibility in logistics operations. Centralizing analytics while decentralizing data collection and accessibility serves as a key benefit of cloud adoption, facilitating efficient logistics management.

AI adoption in logistics drives operational enhancements and solutions identification. Studies indicate that integrating AI can boost profits by up to 5-10% annually, making logistics operations more efficient and smarter in decision-making. Machine learning algorithms embedded within processes significantly reduce manual work, cut costs, and enable intelligent decision-making.

This technology surpasses traditional barcode scanning, enhancing item tracking accuracy throughout the logistics chain. By enabling computers to interpret information from images or videos, computer vision reads damaged, fuzzy, or poorly printed labels with greater precision, elevating efficiency.

The rapid advancements in robotic solutions are revolutionizing logistics and transportation operations. Employing autonomous mobile robots, automated guided vehicles, and drones is becoming increasingly common in various areas such as route planning, warehousing, inventory management, and last-mile deliveries. This trend significantly reduces human involvement while notably enhancing efficiency.

While initially overhyped, Blockchain’s practical application holds significant value for logistics businesses. If correctly developed and implemented, it can serve as a secure transaction ledger, enabling data sharing among different carriers without the risk of manipulation or leakage, fostering trust in the value chain.
In today’s landscape, effective critical data management is paramount. Companies are moving towards standardizing and cleansing data for advanced business analysis, ensuring better visibility of the entire logistics platform, improved forecasting, and optimized last-mile delivery.
With the aim to reduce human intervention, warehouse and logistics automation has seen a surge, utilizing mobile robots, advanced analytics, and computer vision to expedite processes and minimize human error in inventory management.

The complexity of last-mile delivery process prompts the integration of third-party logistics systems and freight transportation services. Though integrating these services with internal order management systems demands substantial time and human resources, it can optimize delivery routes, save time and money and cut transportation spending for transportation companies.
These innovative technologies underscore the competitive advantage they offer, revolutionizing operational paradigms and redefining efficiency across the logistics sector.
When considering transportation software development, it’s vital to recognize that not every business requirement demands an extensive and complex custom logistics software infrastructure. Off-the-shelf logistics software solutions with cloud-based storage, automated backups, and adaptable features can solve diverse needs within the industry.
However, for those seeking a custom logistics solution, meticulous planning of such software becomes paramount. The initial and crucial step involves meticulously estimating the substantial effort this endeavor entails. This entails delineating clear goals, establishing project scopes, and foreseeing the unique requirements necessitated by the custom logistics software ecosystem.
One of the primary challenges inherent in operating a logistics management system lies in its multifaceted nature, composed of distinct software modules serving varying objectives. While delving into the modular structure of an LMS in the following section, it’s imperative to acknowledge that each module requires fundamental operational assets. These assets form the backbone of the system, underscoring the importance of detailed planning, risk management, and comprehensive estimation in guiding the development process effectively.
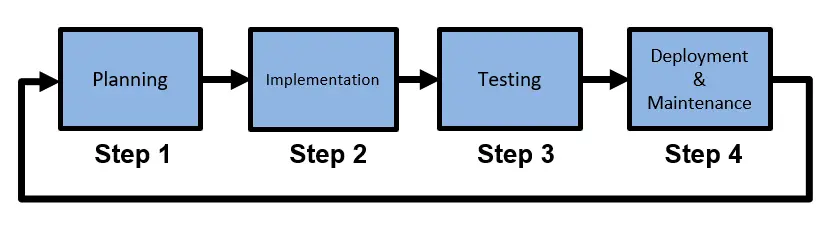
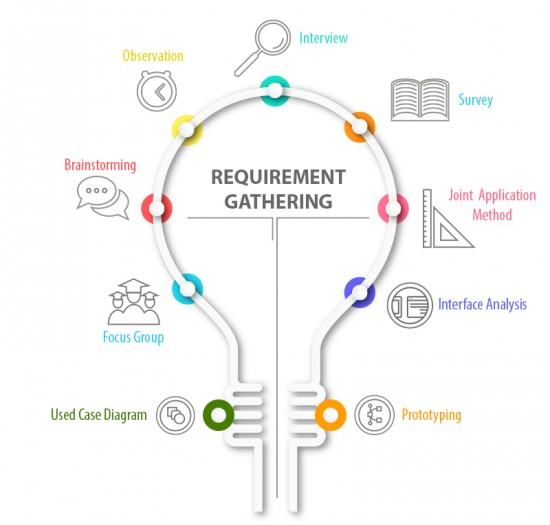
The inception of any successful custom logistics software begins with a meticulous planning phase. As a first step, this discovery phase involves comprehensive brainstorming, gathering crucial requirements, and understanding the business needs . It is imperative to identify the project scope, define objectives, set milestones, and ascertain the essential functionalities the software must encompass. Additionally, in-depth research into market trends, competitor analysis, and user expectations helps lay a solid foundation for the software’s conceptualization.
Once the requirements are gathered, the design phase commences, aiming to craft a blueprint for the logistics software solutions. Architects, designers, and developers collaborate intensively to create a structured plan for logistics software development project encompassing system architecture, database design, user interface (UI), and user experience (UX). The output of this phase includes wireframes, prototypes, and design mock-ups that serve as the visual representation of the envisioned software.
In the design phase of logistics and transportation software, the implementation of a responsive architecture significantly impacts crucial business processes by facilitating real-time data provision to users. For instance, within an inventory management system, this architecture enables the system to instantly validate ingredient availability, conduct automatic unit conversions, and seamlessly record updated data back into the database, thereby streamlining vital business processes.
This exemplifies the prowess of a well-designed transportation management software, guaranteeing accuracy and efficiency in logistics operations. To explore in-depth examples and detailed insights into the role of responsive architecture in custom logistics software development, delve into our comprehensive case study of the Ingenetix project.
With the blueprint in hand, the development team begins the coding and implementation phase. Here, developers bring the software to life by writing code, integrating functionalities, and constructing the various modules based on the outlined specifications. Agile methodologies or other project management frameworks may be applied to ensure iterative development, fostering continuous improvement, flexibility, and adaptation to evolving requirements within the chosen technology stack.

During the pivotal development phase, the Limestone Digital team employs a meticulous approach focused on bringing our clients’ envisioned solutions to life. Here’s a breakdown of our strategies:
Our seasoned developers prioritize freeing up critical decision-making by meticulously automating routine processes. This streamlines operations, allowing businesses to direct their attention towards essential tasks that drive growth and innovation. Implementing process automation not only optimizes workflows but also enhances the efficiency of key functions, such as those found in Transportation Management Software (TMS), ensuring smoother operations and improved decision-making capabilities within logistics frameworks.
Security is paramount in our approach. We strictly adhere to and ensure compliance with rigorous data security standards. This unwavering commitment safeguards our clients’ sensitive information, instilling trust and reliability.
Expanding our automation capabilities unlocks a realm of opportunities, facilitating the integration of novel features and functionalities that enrich the versatility and utility of transportation logistics software, amplifying its overall effectiveness and adaptability.
We strive to develop custom logistics software, which can serve as centralized hubs manufacturing execution systems, providing unparalleled transparency, traceability, and responsiveness across critical business operations. This unified view empowers clients with actionable insights, enabling streamlined decision-making while we continue to develop innovative solutions.
At Limestone Digital, our team remains at the forefront of technological advancements. By leveraging the latest innovations, tools, and methodologies, we ensure the delivery of cutting-edge, efficient, and innovative solutions tailored to our clients’ unique needs.
Following the development stage, rigorous testing and quality assurance processes come into play. Reliable testing methodologies, including unit, integration and system testing, are employed to identify and rectify any discrepancies or bugs within the software applications. After successful quality assurance (QA), the software is released into the production environment. Following deployment, ongoing maintenance and support become necessary to uphold the software’s functionality, address unforeseen issues, and integrate necessary updates or enhancements.
Within the domain of supply chain software development, possessing a robust skill set and specialized expertise are critical elements for success. Professionals in this field, whether in-house or through outsourcing, require a multifaceted skill set and a deep comprehension of logistical intricacies to effectively address challenges and drive advancements in development.
Navigating the evolving landscape of supply chain software development presents a myriad of challenges and innovative opportunities.
The intricate process of integrating diverse systems and technologies within the supply chain ecosystem poses challenges in achieving seamless interoperability and data synchronization.
Safeguarding sensitive supply chain data from cyber threats and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations remain significant challenges in the logistics industry. Implementing an integrated solution addresses these concerns, allowing for robust security measures and adherence to stringent data protection standards.
Transitioning from legacy systems to modern software while ensuring a smooth shift without disruptions presents a considerable challenge.
Consistently improving software to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance overall supply chain efficiency requires ongoing innovation.
Staying abreast of evolving industry trends and swiftly adapting custom software development solutions to meet changing market dynamics and customer expectations is crucial for sustained growth.
Supply chain software developers at Limestone Digital grapple with these challenges while innovating and deploying advanced solutions to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and optimize supply chain performance. Their pivotal role drives the evolution of logistics management by seamlessly integrating technology within supply chain operations.
In conclusion, logistics software development stands at the intersection of technology and logistics, addressing multifaceted challenges within transportation and supply chain management. Its pivotal role encompasses leveraging cutting-edge technologies like AI, IoT, and machine learning to streamline processes, optimize resource utilization, and deliver superior services. Embracing efficiency within the supply chain is fundamental for profitability, customer satisfaction, and maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
The software solutions used in logistics management, including Transportation Management Systems (TMS), Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), and Route Optimization Solutions, among others, offer specialized functionalities to ensure efficient and transparent logistics operations.
Technological advancements continue to drive innovation in logistics, enhancing end-to-end visibility, automating processes, and enabling intelligent decision-making. IoT revolutionizes supply chain visibility, while cloud computing offers scalability and centralizes analytics. AI and machine learning boost profitability, and computer vision enhances accuracy in item tracking.
Supply chain software developers play a crucial role in this landscape, requiring a diverse skill set encompassing logistics expertise, software development proficiency, analytical capabilities, and adaptability to emerging technologies. They navigate challenges like integration complexity, data security, and legacy system transitions while innovating to streamline operations and adapt to industry trends.
The logistics software development process involves meticulous planning, design, coding, testing, deployment, and maintenance, ensuring comprehensive and efficient solutions tailored to the logistics ecosystem. At Limestone Digital, our team’s commitment lies in harnessing innovation, delivering robust, tailored solutions, and optimizing supply chain performance, thus driving the evolution of logistics management software toward enhanced efficiency and competitiveness in the global market.

- 16 mins read
This comprehensive guide will equip you with everything you need to know about eLearning app development services. We'll delve into the world of education app development companies, explore the functionalities that make eLearning solutions effective, and showcase the range of options available to create your ideal learning experience.

- 26 mins read
Discover AI's transformation of e-commerce: enhanced shopping, personalized experiences, and optimized operations in 'E-Commerce 2.0: AI's Role in Online Retail Efficiency.

- 15 mins read
Transform supply chain management in the industry! This guide explores how Machine Learning (ML) revolutionizes the supply chain industry. Discover how ML optimizes forecasting, logistics, and warehouse management for greater efficiency and resilience. Embrace ML and build a more robust supply chain!